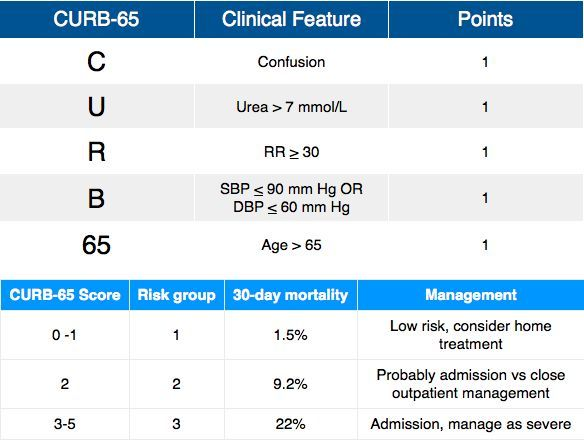
Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is one of the most common conditions encountered in the outpatient setting. The severity of pneumonia can be assessed with a number of different scoring systems. The one most commonly used in the UK is CURB-65 which is convenient and rapid scoring. Based on the scoring system used, the patient can be segregated into those who can be managed as an outpatient, those who need treatment as an inpatient, and furthermore the more severe cases in ICU.
This post is about the patients who can be managed as outpatient and will provide the most significant practical points of great value.
Let’s begin!
1. Infecting pathogens
The most common bacterial causes of CAP in otherwise healthy people include Streptococcus pneumonia, Haemophilus influenzae, and atypical bacteria (Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Legionella pneumophila, and Chlamydia pneumoniae).
Patients with comorbidities (chronic heart, renal, or liver disease, diabetes mellitus, asplenia, and immunosuppression), elderly, or who have recently used antibiotics, in addition to those mentioned, consider other bacteria as well, including gram-negative pathogens (e.g., beta-lactamase-producing H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, Methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus).
For patients with structural lung disease (e.g., advanced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), consider Enterobacteriaceae (e.g., Escherichia coli and Klebsiella species) in the differential.
2. The most preferred antibiotic regimen
Since Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common and virulent bacterial CAP pathogen, the backbone of therapy is beta-lactam. Among beta-lactams, high-dose amoxicillin or amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) are preferred because they remain active against most strains of S. pneumoniae.
A macrolide or doxycycline is added to the beta-lactam to cover atypical bacteria.
3. Other options
If the patient is allergic to penicillin, see if he/she is able to use Cephalosporin (point#5 below). If able to use, then substitute penicillins with 3rd generation cephalosporin.
If the patient cannot tolerate penicillin or cephalosporin, use respiratory fluoroquinolones (Levofloxacin, Moxifloxacin, Gemifloxacin).
Respiratory fluoroquinolones are also used in cases with comorbidities, elderly, structural lung diseases, or patients with recent antibiotics use.
4. Newer antibiotic - Lefamulin & Omadacycline
Lefamulin is a newer antibiotic, belonging to the antibiotic class Pleuromutilin. It is active against most CAP-causing bacteria including S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis, S. aureus, and atypical pathogens.
Lefamulin lacks activity against Enterobacteriaceae (e.g., Klebsiella sp and E. coli) and thus is not used in CAP patients with structural lung disease.
Omadacycline is another newer agent that is active against most CAP pathogens, including Enterobacteriaceae. It can be used as an alternative agent for those patients who cannot tolerate beta-lactams and want to avoid fluoroquinolones.
5. Which Penicillin-allergic patients can use Cephalosporins?
As we know, patients with penicillin allergy also have cross-allergy with cephalosporin.
However, patients with mild non-IgE-mediated reactions (e.g., maculopapular rash) to penicillin or known cephalosporin tolerance can generally use later-generation cephalosporins safely.
Patients with IgE-mediated reactions (hives, angioedema, anaphylaxis) or severe delayed reactions should avoid cephalosporin as well.
6. Macrolides good choice for atypical organisms but avoid if...
Macrolides are best avoided if QTc interval is prolonged, or risk for QTc prolongation (e.g., hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, clinically significant bradycardia, or use of other QT-prolonging agents).
7. Duration of treatment
For most patients, a five-day course of antibiotic therapy is enough. A follow-up visit is indicated within a few days of starting treatment to ensure the response to treatment. Patients who have not responded to therapy after 48 to 72 hours should be re-evaluated.
Have you found this post useful?
Please share your view in the comments and give your valued feedback!